Serial Protocol Building Blocks
The following building blocks are used to describe the subnetwork communication.
Node
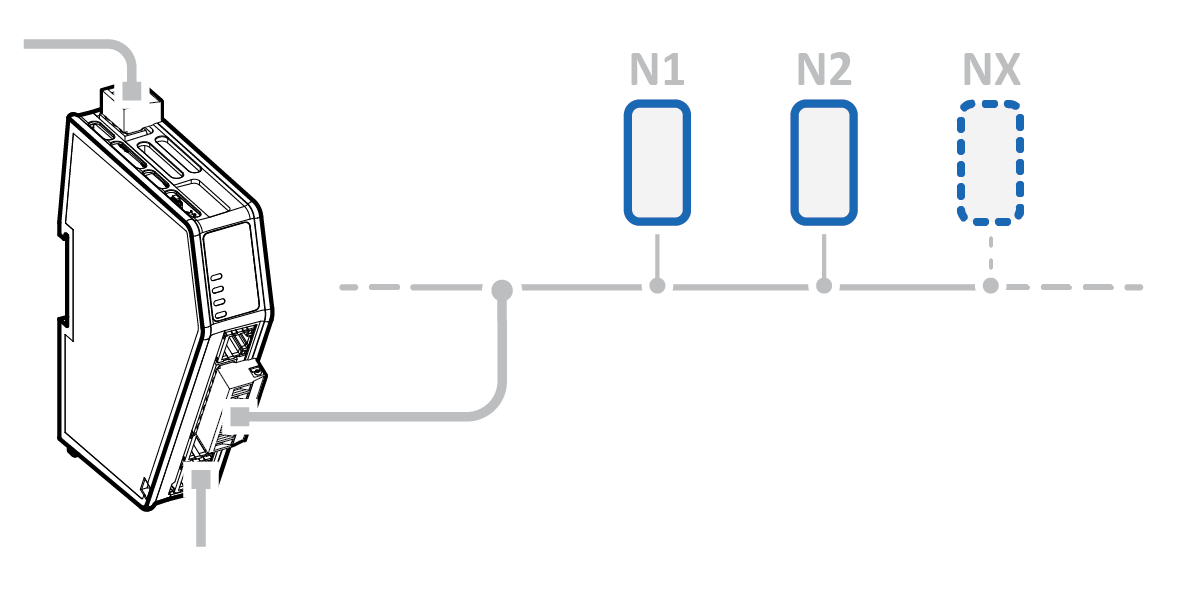 |
A node represents a single device on the subnetwork.
Each node can be associated with a number of transactions.
Nodes and Transactions
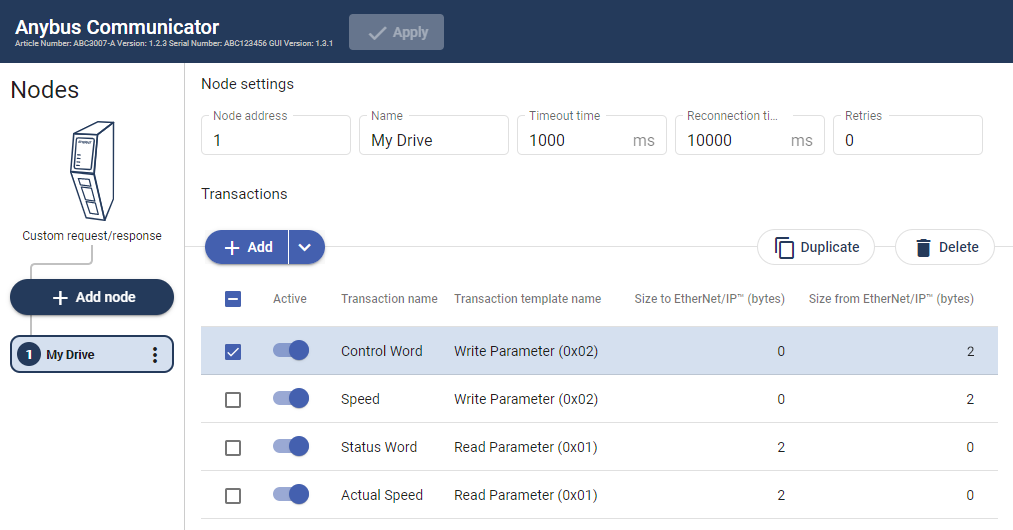 |
Transactions are based on standard Modbus RTU transactions (Modbus RTU serial protocol) or transactions templates (Custom Request/Response or Produce/Consume serial protocol) and define the data to be sent or received.
Each transaction has a number of parameters that need to be configured to define how data is to be sent / received.
Frame Fields
The Frame editor is used to design custom transaction templates.
The Frame editor with Frame fields is available when either the Custom Request/Response or Custom Produce/Consume serial protocol is enabled.
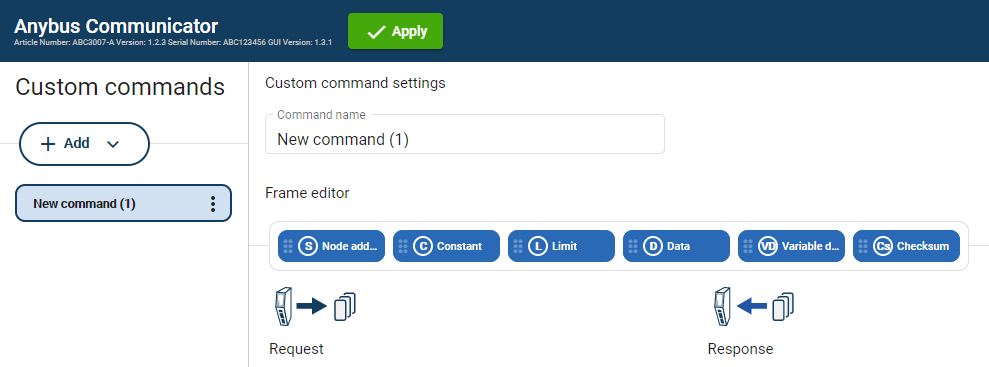 |
Frame fields are low level entities used to compose transactions.
A frame object can represent a:
fixed value, a constant
range of values, limit objects
block of data or a calculated checksum
Transaction Templates
The Transaction templates are available when either the Custom Request/Response or Custom Produce/Consume serial protocol is enabled.
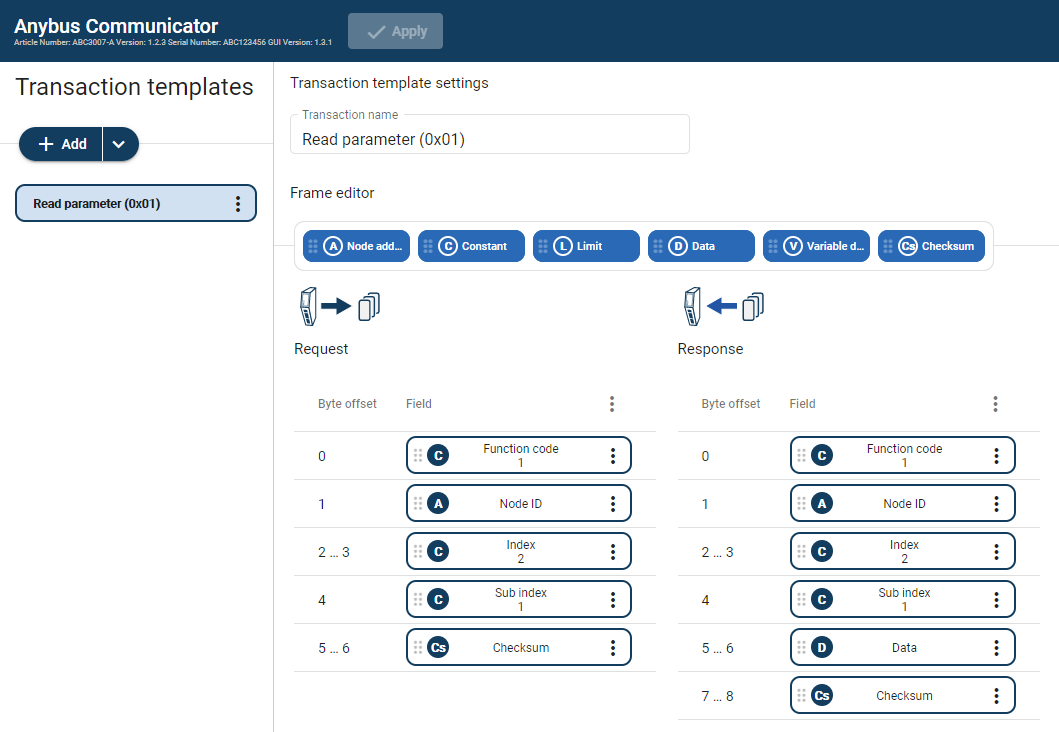 |
A transaction represents a complete serial telegram, and consists of a number of frame fields.
Each frame field is associated with a set of parameters controlling what is transmitted on the subnetwork.
The transaction templates are stored in the Communicator and can be reused multiple times.
If you have a common read transaction. Then you can create one single transaction template for the read transaction and reuse it multiple times times on your node(s).
If you have a function code in your protocol similar to a standard Modbus RTU transaction. Then you can create a transaction template based on the Modbus RTU transaction for the read operation. When you reuse the template on your node(s), you only have to change the function code each time it is used.